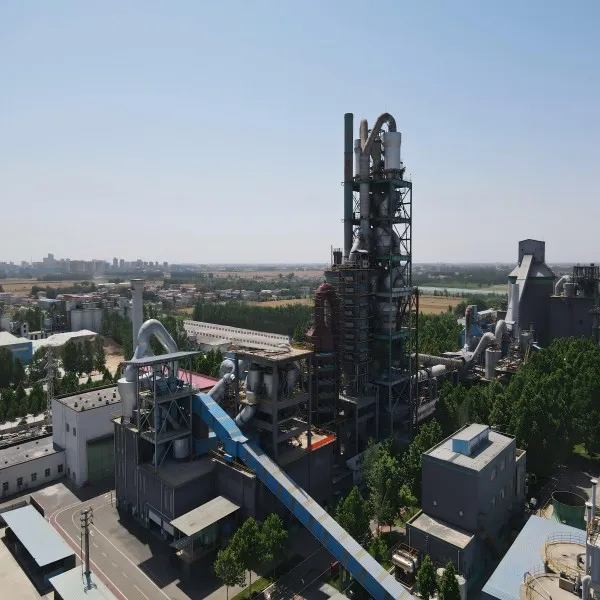
Meeting Emission Standards Through Technological Innovation
With global awareness of environmental protection at an all-time high, industries face increasing pressure to reduce harmful emissions and adopt cleaner technologies. Among the many tools available for pollution control, flue gas desulfurization has emerged as a vital system for achieving environmental compliance. It is particularly effective at limiting sulfur dioxide (SO₂) emissions, one of the primary contributors to acid rain and atmospheric pollution. As governments and regulatory agencies continue to strengthen emission standards, flue gas desulfurization offers an efficient and proven method for industries to meet their obligations while promoting sustainable practices.
Core Function of Flue Gas Desulfurization Systems
Sulfur Dioxide Removal Efficiency
Flue gas desulfurization systems are designed to remove SO₂ from the exhaust gases of combustion systems. These emissions are common in power plants, cement kilns, metal smelters, and other heavy industrial operations that burn fossil fuels. By introducing an alkaline absorbent—typically lime or limestone—into the gas stream, FGD systems facilitate a chemical reaction that transforms SO₂ into stable, non-toxic byproducts.
High-performing systems can eliminate more than 95% of sulfur dioxide emissions. This level of control is critical for meeting national and international environmental regulations that limit sulfur emissions into the atmosphere.
Reduction of Acid Rain Precursors
Sulfur dioxide is a major precursor of acid rain, which results when SO₂ reacts with moisture in the atmosphere to form sulfuric acid. Acid rain damages ecosystems, corrodes buildings, and lowers soil pH. By deploying flue gas desulfurization technologies, industries significantly reduce the release of this harmful gas, thereby minimizing their contribution to acid rain formation.
The reduction of SO₂ helps preserve biodiversity, protect water resources, and maintain soil balance, especially in regions already facing environmental degradation due to industrial activities.
Role in Regulatory Compliance Frameworks
Alignment with National Emission Standards
Many countries have established strict limits on sulfur dioxide emissions through environmental protection agencies or ministries of environment. Flue gas desulfurization systems allow companies to stay within these limits, helping them avoid fines, license revocations, or mandatory shutdowns. These standards often form part of broader air quality programs that address various types of emissions.
Implementing an effective FGD system is not just a regulatory necessity but also a sign of operational responsibility. It demonstrates a proactive commitment to reducing environmental impact and complying with industry best practices.
Meeting International Environmental Agreements
On a global scale, emission reductions are a key part of agreements like the Paris Climate Accord and various regional air quality protocols. Flue gas desulfurization technologies contribute directly to these efforts by enabling countries to lower their industrial SO₂ output. Industrial participants that adopt such systems often benefit from incentives, tax breaks, or certification programs designed to promote cleaner production.
These programs not only support global sustainability but also help position companies as leaders in environmental stewardship.
Benefits for Industrial Operations
Enhanced Public and Regulatory Reputation
In today’s environmentally conscious market, public perception matters. Companies that invest in flue gas desulfurization are often seen as more responsible and forward-thinking. This reputation can attract environmentally minded investors, customers, and partners who prioritize sustainability.
Additionally, compliance with environmental laws builds trust with regulatory authorities, potentially leading to smoother permitting processes and fewer operational restrictions in the future.
Lower Legal and Financial Risks
Non-compliance with environmental standards can lead to substantial penalties, legal disputes, and costly upgrades enforced by law. Installing a reliable flue gas desulfurization system mitigates these risks by ensuring that facilities stay within acceptable emission thresholds at all times.
For industries that operate under tight budgets or sensitive deadlines, this risk reduction is essential. It allows them to maintain continuous operations without interruption or legal jeopardy.
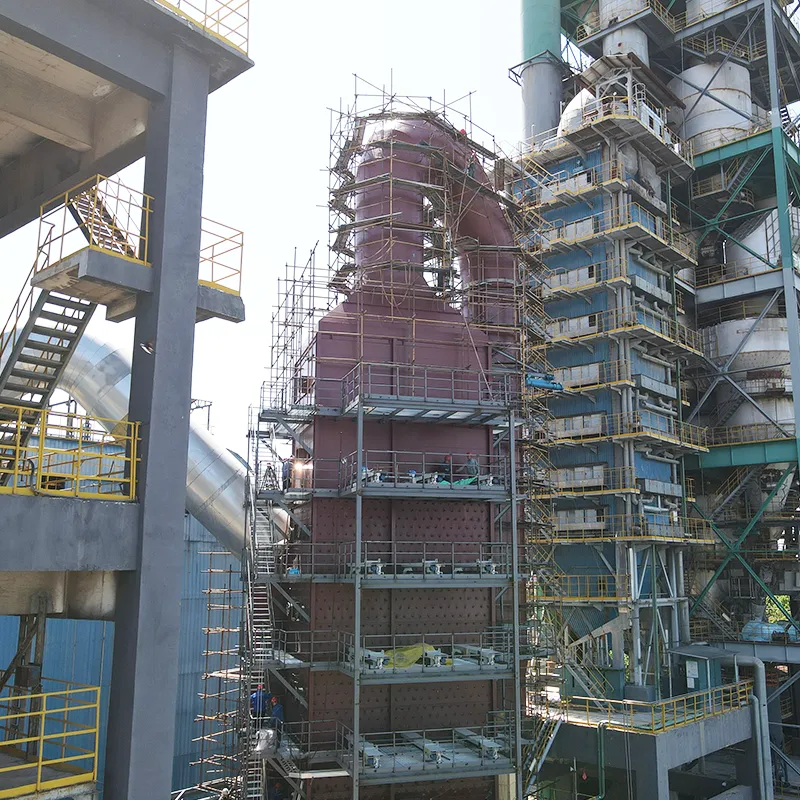

Types of Flue Gas Desulfurization Systems in Use
Wet Scrubber Systems
Wet FGD systems are the most common and effective, especially for large-scale facilities. These systems involve spraying a mixture of limestone and water into the flue gas stream, where it reacts with sulfur dioxide to produce gypsum. The resulting slurry is collected and removed for disposal or recycling.
The high efficiency of wet scrubbers makes them ideal for industries with high sulfur content in their fuels. In addition to compliance benefits, wet FGD systems offer operational consistency and scalability.
Dry and Semi-Dry Alternatives
In facilities where water usage must be minimized, dry and semi-dry flue gas desulfurization options are available. These systems inject a dry or humidified sorbent directly into the gas stream. The resulting byproducts are then collected in a fabric filter or electrostatic precipitator.
Although they generally offer lower SO₂ removal efficiency compared to wet systems, dry FGD systems are easier to install and maintain. They are well-suited to smaller operations or regions with water scarcity challenges.
Environmental and Economic Synergies
Utilization of Byproducts
An often-overlooked advantage of flue gas desulfurization is the potential reuse of its byproducts. Wet FGD systems that produce gypsum can supply the construction industry with materials for drywall and cement manufacturing. This reduces waste and supports a circular economy model.
By turning a pollutant into a usable resource, facilities enhance their environmental performance and create additional revenue streams or cost-saving opportunities.
Support for Long-Term Sustainability Goals
Flue gas desulfurization aligns with many companies’ environmental, social, and governance (ESG) objectives. It provides measurable results in air quality improvement and greenhouse gas reduction, contributing to long-term sustainability targets.
As climate risk assessments become more integrated into investment decisions, companies that utilize FGD technology are better positioned to attract funding and maintain stakeholder confidence.
Integrating FGD into Broader Emission Control Systems
Combined Pollution Control Strategies
In many industrial facilities, flue gas desulfurization is used alongside other pollution control technologies like selective catalytic reduction (SCR) for nitrogen oxides and particulate filters. These integrated systems allow facilities to manage multiple emission types simultaneously and more effectively.
With the right design, integration improves overall efficiency, reduces energy consumption, and simplifies compliance with multifaceted regulatory standards.
Automation and Monitoring Advancements
Modern flue gas desulfurization systems increasingly incorporate automation and data analytics tools. These technologies enable real-time monitoring of emission levels, optimize sorbent usage, and alert operators to system issues before they become critical.
This advancement not only improves system performance but also ensures continuous compliance through precise, data-driven operation.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the primary function of flue gas desulfurization?
Flue gas desulfurization removes sulfur dioxide from industrial exhaust gases to reduce air pollution and help facilities comply with environmental regulations.
Are flue gas desulfurization systems mandatory for all industries?
Not all industries require FGD systems, but they are essential in sectors like power generation, metallurgy, and cement manufacturing where sulfur emissions are high.
Can FGD systems be added to existing plants?
Yes. Many flue gas desulfurization technologies can be retrofitted into existing operations with proper engineering, especially in facilities aiming to upgrade for compliance.
Do flue gas desulfurization systems require frequent maintenance?
Routine maintenance is necessary but not overly intensive. Regular inspections, sorbent replenishment, and cleaning help maintain the efficiency of FGD systems.
Table of Contents
- Meeting Emission Standards Through Technological Innovation
- Core Function of Flue Gas Desulfurization Systems
- Role in Regulatory Compliance Frameworks
- Benefits for Industrial Operations
- Types of Flue Gas Desulfurization Systems in Use
- Environmental and Economic Synergies
- Integrating FGD into Broader Emission Control Systems
- Frequently Asked Questions