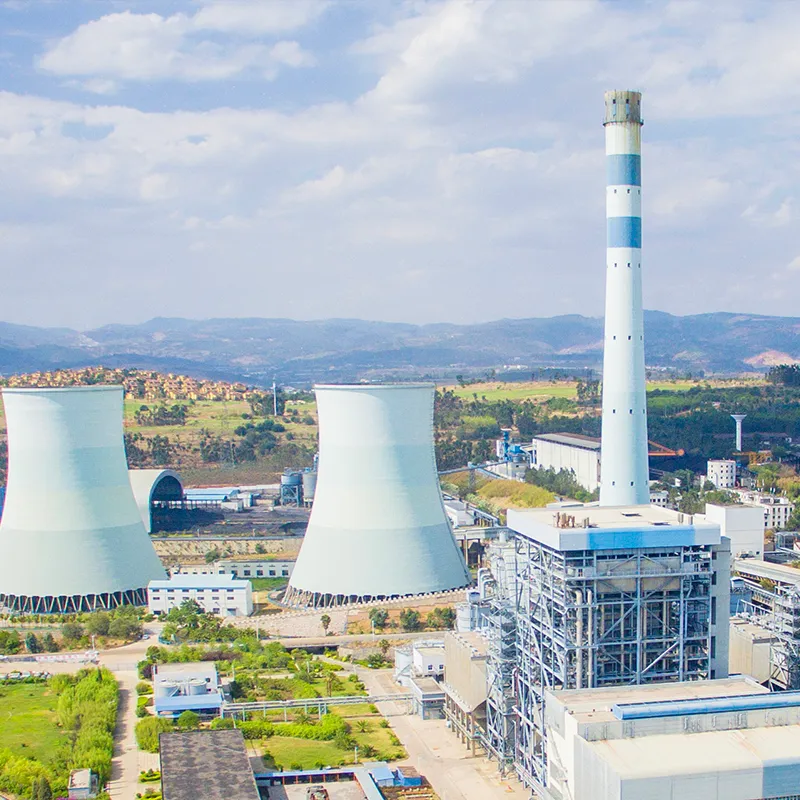
1. Desulfurization Challenges in Petrochemical Plants
Petrochemical complexes operate under some of the most demanding flue gas conditions in the industrial sector. Unlike conventional power plants, petrochemical facilities consist of multiple emission sources, including heaters, furnaces, boilers, sulfur recovery units (SRU), hydrogen production units, and various off-gas systems. Each unit generates flue gas with different temperatures, sulfur concentrations, moisture levels, and impurity profiles.
Typical challenges faced by petrochemical operators include:
Fluctuating SO₂ concentrations due to variable feedstock quality
High moisture and corrosive components in flue gas
Limited space for retrofit projects
Strict emission limits driven by environmental regulations and ESG commitments
High expectations for long-term operational stability
Traditional desulfurization technologies, such as limestone-gypsum wet FGD or sodium-based systems, can technically meet emission standards but often struggle with high operating costs, scaling issues, and waste byproduct management when applied in complex petrochemical environments.
As a result, petrochemical companies are increasingly evaluating ammonia-based flue gas desulfurization (Ammonia FGD) as a more adaptable and economically sustainable solution.
2. Why Petrochemical Flue Gas Requires a Different Desulfurization Approach
Petrochemical flue gas differs fundamentally from coal-fired power plant flue gas in several aspects:
Lower but highly variable sulfur content
Higher process integration requirements
Greater sensitivity to pressure drop and system downtime
Many petrochemical units operate continuously, and even short shutdowns can lead to significant production losses. Therefore, any desulfurization system must offer:
Fast response to load changes
Stable performance under fluctuating operating conditions
Minimal interference with existing process units
Ammonia-based desulfurization meets these requirements through liquid-phase reactions with high mass transfer efficiency, enabling rapid sulfur absorption even under variable gas conditions.
3. How Ammonia-Based Desulfurization Works in Petrochemical Applications
In an ammonia-based desulfurization system, SO₂ in flue gas reacts with ammonia solution to form ammonium sulfite and ammonium sulfate. With proper oxidation control, the final product is high-purity ammonium sulfate, a widely used nitrogen fertilizer.
Key reaction advantages include:
Fast chemical reaction rate
High sulfur removal efficiency even at low SO₂ concentrations
Stable performance across wide temperature ranges
For petrochemical plants, ammonia is often readily available as part of existing processes or logistics systems, making integration relatively straightforward.
4. Key Advantages of Ammonia FGD for Petrochemical Plants
4.1 High Desulfurization Efficiency with Ultra-Low Emissions
Modern ammonia-based systems can achieve SO₂ removal efficiencies above 98%, enabling outlet concentrations well below international emission limits. This makes ammonia FGD suitable not only for compliance today but also for future tightening of environmental regulations.
4.2 No Solid Waste Disposal Burden
Unlike limestone-based systems that generate large volumes of gypsum requiring disposal or off-site sales, ammonia FGD produces marketable ammonium sulfate. This transforms desulfurization from a cost center into a resource recovery process.
For petrochemical operators focused on circular economy principles, this advantage is particularly attractive.
4.3 Lower Operating Costs Over the Project Lifecycle
Although ammonia-based systems may require careful design and control, their overall lifecycle cost is often lower than conventional alternatives due to:
Reduced reagent consumption
Minimal scaling and fouling
Lower maintenance frequency
Revenue from byproduct sales
In large petrochemical complexes, these savings become increasingly significant over long-term operation.
4.4 Strong Adaptability to Complex Flue Gas Conditions
Petrochemical flue gas may contain:
Trace hydrocarbons
Acidic components
Fine particulates
Advanced ammonia-based systems incorporate multi-stage gas-liquid separation and purification, ensuring stable operation without secondary pollution such as aerosol formation or visible plume issues.
5. Addressing Traditional Concerns About Ammonia Desulfurization
Historically, some petrochemical companies hesitated to adopt ammonia-based desulfurization due to concerns about:
Ammonia slip
Aerosol formation
Corrosion risks
However, modern engineering solutions have largely resolved these issues.
Advanced systems use:
Precise ammonia injection control
Multi-stage mist eliminators
Optimized oxidation and pH management
As a result, ammonia slip can be controlled at below 1 mg/Nm³, while aerosol formation is effectively suppressed.
6. Integration with Existing Petrochemical Infrastructure
One of the strongest advantages of ammonia FGD is its compatibility with existing petrochemical systems.
It can be integrated with:
Waste heat recovery units
Tail gas treatment systems
Centralized flue gas treatment facilities
The relatively low pressure drop of ammonia-based absorbers ensures minimal impact on upstream process units, a critical factor in continuous petrochemical production.
7. Environmental and ESG Benefits
From an ESG perspective, ammonia-based desulfurization supports multiple sustainability objectives:
Significant reduction of sulfur emissions
Conversion of pollutants into valuable products
Reduced solid waste generation
Improved overall resource efficiency
These benefits help petrochemical companies strengthen their environmental credentials while maintaining operational competitiveness.
8. A Long-Term Solution for the Petrochemical Industry
As petrochemical plants face increasing pressure to reduce emissions without sacrificing productivity, ammonia-based desulfurization offers a balanced solution combining environmental performance, economic viability, and operational reliability.
With continuous technological improvements, ammonia FGD is no longer an experimental option—it is a mature and proven technology suitable for large-scale petrochemical applications worldwide.
Table of Contents
- 1. Desulfurization Challenges in Petrochemical Plants
- 2. Why Petrochemical Flue Gas Requires a Different Desulfurization Approach
- 3. How Ammonia-Based Desulfurization Works in Petrochemical Applications
- 4. Key Advantages of Ammonia FGD for Petrochemical Plants
- 5. Addressing Traditional Concerns About Ammonia Desulfurization
- 6. Integration with Existing Petrochemical Infrastructure
- 7. Environmental and ESG Benefits
- 8. A Long-Term Solution for the Petrochemical Industry