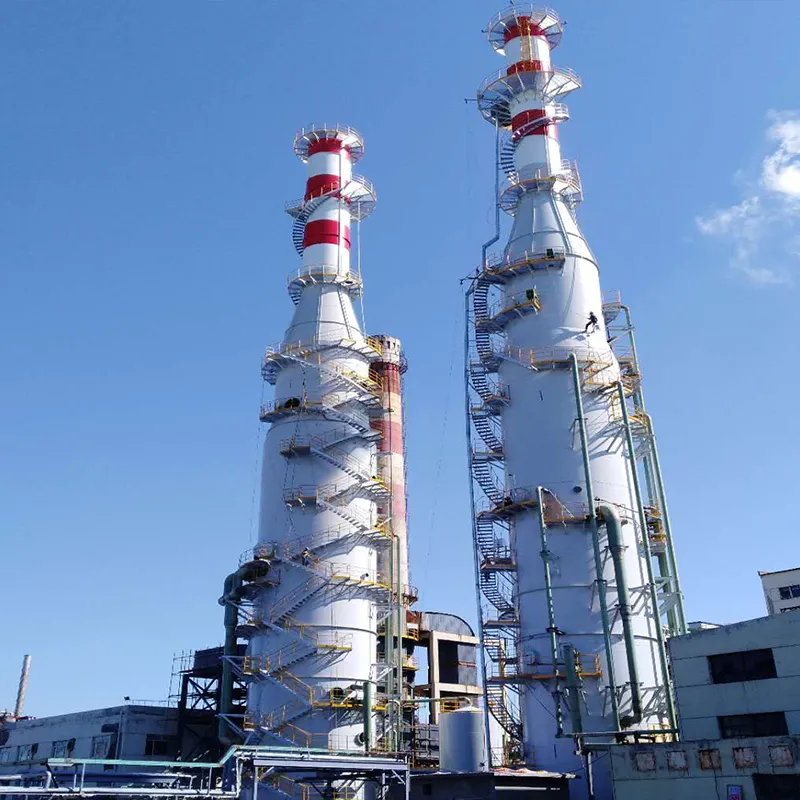
Discover ammonia-based desulfurization technology for industrial SO₂ removal, reducing emissions while supporting sustainable and cost-effective solutions.
Introduction
The growing industrial demand for cleaner energy solutions has placed environmental sustainability at the forefront of operational strategies. Industries worldwide face increasing pressure to minimize sulfur dioxide (SO₂) emissions due to stricter environmental regulations. Among the most advanced and eco-friendly technologies is ammonia-based flue gas desulfurization (NH₃-FGD). This innovative approach not only reduces harmful emissions but also produces valuable byproducts that can be utilized in various industrial applications.
Core Principles of Ammonia-Based Desulfurization
Chemical Reactions and Mechanisms
Ammonia-based desulfurization operates on a simple yet highly effective chemical principle. Sulfur dioxide in flue gas reacts with ammonia to form ammonium sulfate ((NH₄)₂SO₄), a crystalline compound widely used as a fertilizer. The overall reaction ensures that nearly all SO₂ is captured, significantly reducing air pollution and acid rain formation.
Types of NH₃-FGD Systems
There are mainly two types of ammonia-based desulfurization systems: wet ammonia FGD and dry ammonia FGD. Wet systems employ a liquid ammonia solution to absorb SO₂, achieving very high removal efficiencies. Dry systems, conversely, inject ammonia and water mist into the flue gas, which reacts with SO₂ to form a solid ammonium salt. Both systems are selected based on plant size, emission levels, and operational requirements.
Environmental Benefits and Regulatory Compliance
Reduction of Acid Rain-Causing Emissions
Sulfur dioxide is a major contributor to acid rain, which negatively affects soil, water, and forest ecosystems. By implementing NH₃-FGD, industrial facilities can drastically reduce SO₂ emissions, thereby mitigating the environmental impact.
Meeting International Emission Standards
Global environmental regulations increasingly demand low SO₂ emissions. Ammonia-based desulfurization systems help facilities comply with these stringent standards, enhancing corporate responsibility and public trust.
Economic and Operational Considerations
Cost Efficiency
Although ammonia-based desulfurization requires initial capital investment, long-term benefits are substantial. Facilities save on potential fines, generate saleable ammonium sulfate, and often qualify for environmental subsidies.
Operational Reliability
Modern NH₃-FGD systems are designed for continuous operation with minimal downtime. Advanced monitoring and automation allow precise control over the desulfurization process, ensuring consistent performance.
Integration with Sustainable Energy Goals
By reducing emissions, ammonia FGD facilitates smoother integration with renewable energy initiatives. Even during the transition from fossil fuels to clean energy, plants equipped with NH₃-FGD minimize environmental impact, supporting global sustainability objectives.
Technological Advancements
Automation and Digital Control
New systems feature automated controls, real-time monitoring, and predictive maintenance tools. This ensures high efficiency and operational reliability while reducing human error and labor costs.
Compact and Modular Designs
Modern NH₃-FGD units are increasingly modular, allowing for easy installation in existing facilities without major structural modifications.
Applications Across Industries
Ammonia-based desulfurization is not limited to coal-fired power plants; it extends to petrochemical plants, metal smelters, and waste incineration facilities. Each sector benefits from cleaner emissions and resource recovery.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the main product of ammonia desulfurization?
The main product is ammonium sulfate ((NH₄)₂SO₄), which can be used as fertilizer.
Is ammonia FGD more efficient than limestone-gypsum systems?
Yes, NH₃-FGD often achieves higher SO₂ removal efficiency and produces a valuable byproduct.
Can NH₃-FGD be retrofitted into existing plants?
Yes, modular designs and flexible configurations allow retrofitting into existing infrastructure.
Conclusion
Ammonia-based desulfurization represents a sustainable, economically viable solution for industries striving to reduce emissions. By combining environmental benefits, regulatory compliance, and operational efficiency, NH₃-FGD is a key technology in the transition toward cleaner industrial energy.