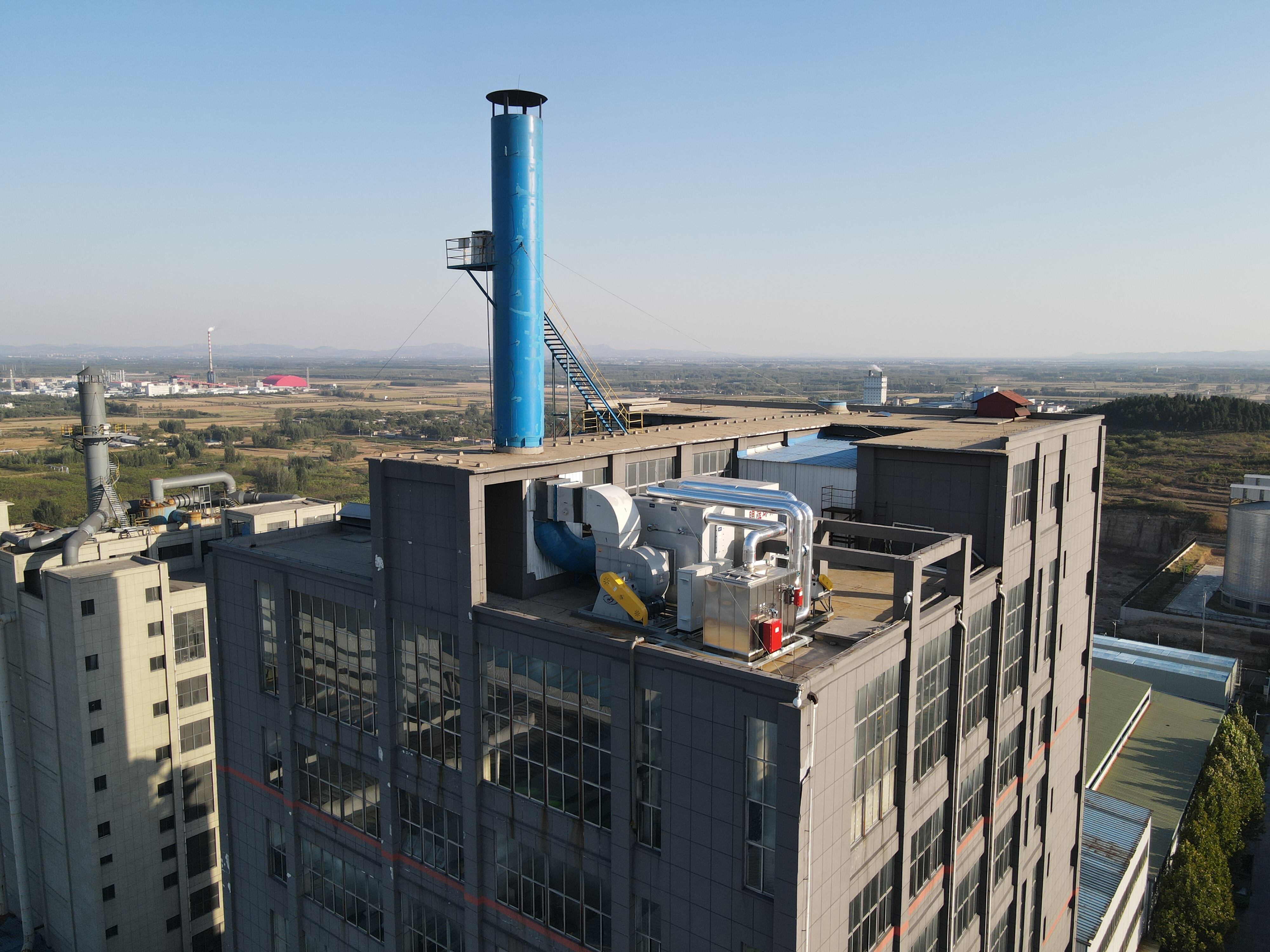
Metallurgy is another major contributor to VOC pollution, especially during the sintering process. VOC formation depends heavily on:
Fuel composition
Organic additives
Temperature profiles
Airflow patterns
Main Mechanisms of VOC Formation
Combustion of coal and coke
Volatilization of organic binders
Decomposition of oily residues on metal surfaces
Thermal cracking of complex hydrocarbons
Key Characteristics
VOC generation occurs mainly between 100°C and 900°C
Sintering bed thickness usually 100–200 mm
VOCs condense into fine particles upon cooling, contributing to secondary particulate pollution
Effective control requires high-temperature oxidation or catalytic treatment systems.
3. VOC Emissions in Packaging and Printing Industries
Printing and packaging are among the largest VOC-emitting sectors in light manufacturing.
Sources of VOCs
Solvent-based inks
Printing solvents
Adhesives
Coating formulations
Cleaning agents
Evaporation in drying ovens
Industries Most Involved
Plastic flexible packaging
Paper packaging
Metal packaging
Gravure and flexographic printing
Common Industrial Solvents
Ethyl acetate
Toluene
Methyl ethyl ketone (MEK)
Isopropyl alcohol
Due to low boiling points, VOCs evaporate rapidly during printing and curing, requiring efficient collection and treatment.
4. VOC Emissions in Coating and Surface Finishing
Coating industries involve multiple stages, each releasing organic vapors:
Typical Coating Processes
Paint mixing
Spray application
Leveling and flash-off
Drying and curing
Industries involved include:
Furniture
Metal fabrication
Automotive manufacturing
Aviation
Shipbuilding
Rail transportation
Equipment manufacturing
Solvent evaporation is the primary emission source, especially during spraying and baking.
Effective VOC Treatment Technologies
1. Regenerative Thermal Oxidizer (RTO)
High destruction rate: 98%
Suitable for high-concentration, stable VOC streams
Converts VOCs to CO₂ and H₂O
Highly efficient heat recovery reduces operational cost
2. Catalytic Oxidation (RCO)
Lower temperature than RTO
Suitable for clean, low-sulfur gas streams
Sensitive to sulfur, chlorine, and heavy metals
3. Activated Carbon Adsorption
Ideal for low-concentration, high-airflow VOCs
Can be combined with desorption + RTO
Effective for benzene, toluene, xylene
4. Condensation
Used when VOC concentration is high or compounds have low boiling points
Often applied in chemical and solvent recovery plants
5. Biological Treatment
Used for biodegradable compounds like alcohols, aldehydes
Eco-friendly but limited for complex hydrocarbons
Environmental and Regulatory Drivers
Why controlling VOCs is essential?
Health risks: VOCs can cause respiratory issues, neurological effects, and cancer
Environmental impacts: contribute to ozone formation and secondary PM2.5
Regulatory pressure: international standards now enforce strict emission caps
Corporate sustainability: VOC control supports ESG goals and public trust
FAQ
What makes VOC treatment challenging?
Their chemical diversity and variability in concentration, humidity, and air volume.
Which industries produce the most VOC emissions?
Coal chemical, petrochemical, printing, coating, and metallurgy.
Is RTO the best technology for VOC treatment?
It is the most universal solution for mixed and high-concentration VOCs.
Conclusion
VOCs are among the most challenging and widespread industrial pollutants, impacting public health and environmental quality. Understanding their sources—from coal chemical plants to printing and coating lines—is essential for designing effective treatment systems. Technologies such as RTO, catalytic oxidation, adsorption, and condensation offer robust solutions tailored to different industrial conditions.
As environmental expectations continue to rise, investing in advanced VOC treatment is no longer optional—it is a strategic necessity that supports long-term sustainability, regulatory compliance, and operational excellence.