Learn about advanced tire pyrolysis systems that convert waste tires into oil, carbon black, and gas, optimizing efficiency and minimizing environmental impact.
Introduction
The rapid increase in global tire production has led to a mounting challenge in waste management. Traditional disposal methods such as landfilling or burning are not sustainable. Advanced tire pyrolysis systems have emerged as a highly efficient solution for recycling waste tires while producing energy and industrial byproducts. These systems combine chemical engineering principles, advanced reactor design, and environmental compliance to deliver maximum efficiency.
How Tire Pyrolysis Works
Thermochemical Process
Tire pyrolysis involves heating shredded tires to temperatures between 400°C and 600°C in an oxygen-free environment. During this process, polymers decompose into smaller hydrocarbons, generating:
Pyrolysis oil
Solid carbon black
-
Pyrolysis gas
The process also produces minimal residue, reducing environmental footprint.
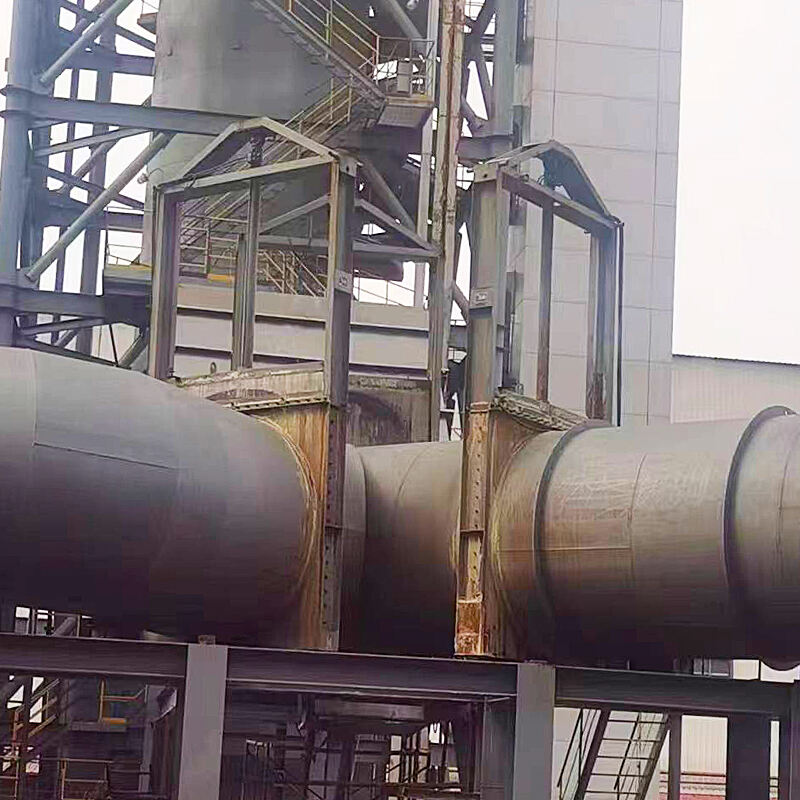
System Design and Optimization
Reactor Types
Common reactor types include:
Batch reactors: suitable for small-scale operations
Continuous reactors: ideal for industrial-scale production, offering higher throughput
Rotary drum reactors: ensure uniform heating and improved oil yield
Temperature and Retention Time Control
Precise control over temperature and gas retention time is critical to optimize product composition and maximize oil and carbon black yield.
Environmental Compliance
Emission Control
Modern systems are equipped with scrubbers and filters to reduce particulate and volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions, ensuring compliance with environmental regulations.
Waste Gas Utilization
The combustible gas produced during pyrolysis can be recycled to supply heat for the reactor, minimizing external energy consumption and lowering operational costs.
Economic Benefits
Multiple Revenue Streams
Pyrolysis oil: industrial fuel or chemical feedstock
Carbon black: material for rubber and asphalt production
Pyrolysis gas: energy for plant operation
Return on Investment
While initial capital investment is significant, the revenue from multiple byproducts combined with reduced waste disposal costs makes tire pyrolysis financially attractive.
Technological Advancements
Automation and Monitoring
Automated control systems optimize heating, feeding, and condensation processes. Digital monitoring ensures safety, efficiency, and consistent product quality.
Modular and Scalable Designs
Modern pyrolysis units are modular, enabling easy installation, scalability, and flexibility to adapt to changing production needs.
Industrial Applications
Tire pyrolysis technology is applied in:
Industrial recycling plants
Waste management facilities
Energy recovery operations
Asphalt and rubber industries
Conclusion
Advanced tire pyrolysis systems represent a sustainable and profitable method to manage waste tires. By integrating efficiency, safety, and environmental compliance, these systems transform waste into valuable resources, contributing to circular economy goals and industrial sustainability.